Calcined Clay (Kaolin)


Calcined clay is produced when raw kaolin or more popularly known as Clay or China Clay is fired enough to reduce its crystalline water content via a process known as Calcination. The calcination process increases whiteness and hardness of the Clay, improves its electrical properties, and alters the size and shape of the kaolin particles. Calcination makes the powder whiter and more chemical inert. Calcined Kaolin is used as a functional extender in paint. Calcined kaolin has proven to be an excellent extender for titanium dioxide (white) pigment in paint.
A thermally engineered pigment designed for high light scattering performance. Commonly used as a cost-effective replacement for TiO2 in many applications
Khandela Minerals calcined clays are structured clays that are formed by treating select hydrous clay at high temperatures to form agglomerates that have a controlled pore structure that maximises light scattering. Calcined clay is generally used as a cost-effective opacifier and high light scatter pigment that provides excellent fibre coverage and bulk to the coating layer. It has been successfully used for several decades as a TiO2 extender.
Various Applications of Kaolin

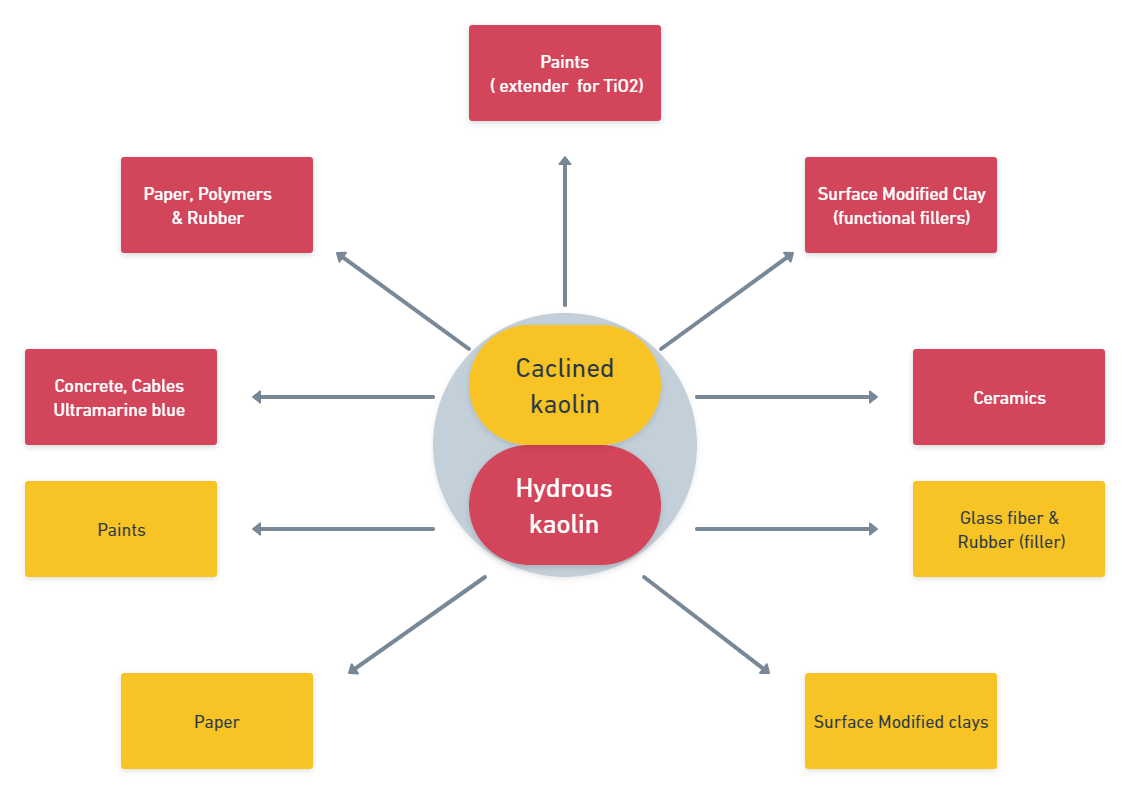
Key properties of Kaolin

- High Whiteness & Brightness
- Particle Size Distribution
- Opacity (Hiding Power)
- Electrical Properties
- Mechanical Properties
APPLICATIONS